Adozin Adenozin Injection Imported in Pakistan
Overview of Adozin Injection
Adozin is an injectable solution containing adenosine, primarily used for the rapid conversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) to normal sinus rhythm. It is available in Pakistan and is intended for use in hospital settings under strict medical supervision.
Composition and Dosage
Each vial of Adozin contains:
- Active Ingredient: Adenosine 3 mg/mL
- Total Volume: 2 mL per vial (6 mg total)
The solution is clear and colorless, free from visible particles. It is administered as a rapid intravenous (IV) bolus, typically starting with a dose of 3 mg for adults, with the possibility of repeat doses if necessary.
Indications for Use
Adozin is indicated for:
- Conversion of PSVT: Effective in restoring normal sinus rhythm in patients experiencing PSVT, including those with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome.
- Diagnostic Aid: Helps in diagnosing broad or narrow complex supraventricular tachycardias by slowing AV conduction, although it does not convert atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation.
Administration Guidelines
Adozin should be administered by healthcare professionals in a controlled environment, with cardiorespiratory resuscitation equipment readily available. The injection should be followed by a saline flush to ensure proper delivery. Continuous monitoring of the patient’s heart rhythm and vital signs is essential during administration.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects may include dizziness or drowsiness, necessitating caution in activities requiring alertness. Serious adverse effects can occur, such as severe bradycardia or hypotension, and immediate medical attention is required if these occur. Adozin is contraindicated in patients with certain heart conditions, including Long QT syndrome.
Description
Overview of Adozin Injection
Adozin is an injectable solution containing adenosine, primarily used for the rapid conversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) to normal sinus rhythm. It is available in Pakistan and is intended for use in hospital settings under strict medical supervision.
Composition and Dosage
Each vial of Adozin contains:
- Active Ingredient: Adenosine 3 mg/mL
- Total Volume: 2 mL per vial (6 mg total)
The solution is clear and colorless, free from visible particles. It is administered as a rapid intravenous (IV) bolus, typically starting with a dose of 3 mg for adults, with the possibility of repeat doses if necessary.
Indications for Use
Adozin is indicated for:
- Conversion of PSVT: Effective in restoring normal sinus rhythm in patients experiencing PSVT, including those with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome.
- Diagnostic Aid: Helps in diagnosing broad or narrow complex supraventricular tachycardias by slowing AV conduction, although it does not convert atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation.
Administration Guidelines
Adozin should be administered by healthcare professionals in a controlled environment, with cardiorespiratory resuscitation equipment readily available. The injection should be followed by a saline flush to ensure proper delivery. Continuous monitoring of the patient’s heart rhythm and vital signs is essential during administration.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects may include dizziness or drowsiness, necessitating caution in activities requiring alertness. Serious adverse effects can occur, such as severe bradycardia or hypotension, and immediate medical attention is required if these occur. Adozin is contraindicated in patients with certain heart conditions, including Long QT syndrome.
Key Benefits of Adozin Injection
- Rapid Conversion of PSVT: Adozin is primarily used for the rapid conversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) to normal sinus rhythm, making it critical in emergency cardiac care.
- Diagnostic Aid: It serves as a pharmacologic stress agent for myocardial perfusion imaging, helping to assess heart function and diagnose various cardiac conditions.
- Short-acting: Adozin has a very short half-life, allowing for quick action and rapid resolution of effects, which is particularly beneficial in acute settings.
- Minimal Side Effects: While side effects can occur, they are often transient and manageable, allowing for effective treatment with careful monitoring.
- Hospital Use: Administered under medical supervision, Adozin ensures patient safety during its use, particularly in emergency situations.
Key Ingredients of Adozin Injection
- Active Ingredient: Adenosine is the primary active component in Adozin, responsible for its therapeutic effects on heart rhythm and vascular dilation.
- Concentration: Adozin is available in multiple concentrations, such as 3 mg/mL and 250 mg/50 mL, catering to different clinical needs.
- Formulation: The injection is typically provided as a clear, colorless solution, ensuring purity and effectiveness.
- Branding: Adozin is marketed under various brand names, including Adenocard and Adenoscan, depending on the manufacturer.
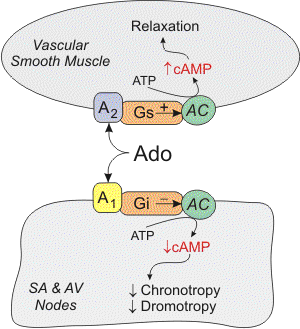
Mechanism of Action of Adozin Injection
Adozin, which contains adenosine, exerts its pharmacological effects primarily through the activation of specific purine receptors in the heart and vascular smooth muscle. Here are the key aspects of its mechanism of action:
1. Receptor Activation
- A1 Receptors: Adenosine binds to A1 receptors located in the atrioventricular (AV) node of the heart, leading to a decrease in conduction velocity. This action helps interrupt re-entry pathways and restore normal sinus rhythm in conditions like paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) .
- A2 Receptors: Activation of A2 receptors results in peripheral vasodilation. This effect is mediated by the relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, which can decrease blood pressure and increase coronary blood flow .
2. Calcium Current Modulation
Adenosine may inhibit the slow inward calcium current in cardiac cells, which reduces calcium uptake. This modulation contributes to its negative chronotropic (slowing heart rate), dromotropic (slowing conduction through the heart), and inotropic (decreasing force of contraction) effects .
3. Vasodilation and Blood Flow
Adenosine causes vasodilation, which increases blood flow to the myocardium (heart muscle) while having a lesser effect on stenotic (narrowed) coronary arteries. This differential effect is important for assessing coronary artery disease during diagnostic tests like myocardial perfusion imaging .
4. Intracellular Metabolism
Once inside the cell, adenosine is rapidly phosphorylated to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) or deaminated to inosine. These metabolites do not have vasoactive properties but are involved in cellular energy metabolism .
5. Elimination
Adenosine is cleared from the plasma primarily through cellular uptake, with a very short half-life of less than 10 seconds in whole blood. This rapid clearance is crucial for its use in acute settings, allowing for quick termination of its effects once the infusion is stopped .
Chemical Structure
- Molecular Formula: C10H13N5O4
- Structural Representation: The chemical structure can be represented as follows:Adenosine Structure
- InChI Key:
OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N
Key Features
- Purine Base: The purine component consists of a fused double-ring structure, which is characteristic of nucleotides.
- Ribose Sugar: The ribose sugar is a five-carbon sugar that is attached to the nitrogenous base, forming the nucleoside adenosine.
N / \ C C // \\ C N | | C——C \ / C–C / \ O N \ / C–C / \ O O
Key Precautions for Adozin Injection
- Medical Supervision: Adozin should only be administered in a hospital setting by trained healthcare professionals who can monitor the patient closely for adverse effects.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Inform your doctor about any history of heart problems, such as unstable angina, recent heart attack, or cardiovascular instability, as these conditions may increase the risk of severe complications during administration.
- Drug Interactions: Avoid concurrent use with certain medications, including:
- Caffeine: Can diminish the therapeutic effect of Adozin. Avoid caffeine-containing foods and drinks, such as coffee, tea, and cola, before receiving the injection.
- Theophylline and xanthines: These can antagonize the action of adenosine.
- Carbamazepine and Digoxin: These may enhance the adverse effects of adenosine, particularly the risk of higher degree heart block.
- Monitoring for Side Effects: Be vigilant for side effects such as chest pain, discomfort, nausea, or sweating. Report any unusual symptoms to a healthcare professional immediately.
- Contraindications: Adozin is contraindicated in patients with second- or third-degree AV block, sinus node disease, or known hypersensitivity to adenosine.
Dietary Restrictions
- Caffeine: As mentioned, do not consume caffeine in any form (including medications, foods, and beverages) before receiving Adozin, as it can interfere with the drug’s effectiveness.
- Alcohol and Tobacco: Avoid alcohol and tobacco use around the time of administration, as these can potentially interact with the medication and exacerbate side effects.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Always discuss any dietary restrictions or concerns with your healthcare provider prior to receiving Adozin to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Major Drug Interactions
- Caffeine: Caffeine and other methylxanthines can antagonize the effects of adenosine, potentially diminishing its therapeutic efficacy. Patients are advised to avoid caffeine-containing products for at least 24 hours before administration of Adozin.
- Digoxin: The combination of digoxin and adenosine may enhance the risk of bradycardia and higher degree heart block. Monitoring is recommended when these drugs are used together.
- Carbamazepine: This anticonvulsant can increase the risk of adverse effects from adenosine, particularly higher degree heart block. A lower initial dose of adenosine may be considered in patients taking carbamazepine.
- Dipyridamole: This medication may enhance the cardiovascular effects of adenosine. It is recommended to withhold dipyridamole before administering adenosine for pharmacologic stress testing to avoid prolonged effects of adenosine.
- Bradycardia-Causing Agents: Adozin may enhance the bradycardic effects of other medications that also cause bradycardia, such as beta-blockers (e.g., atenolol, metoprolol) and certain antiarrhythmics. Close monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure is advised when used in conjunction with these agents.
Minor Interactions
- Other Antiarrhythmics: Medications like sotalol and propranolol may interact with adenosine, necessitating caution and monitoring during concurrent use.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants may also have interactions with adenosine, requiring careful consideration and monitoring of the patient’s response.
Alcohol and Food Interactions
Adozin has three known interactions with alcohol and food, which can affect its pharmacological effects. It is generally advisable to avoid alcohol around the time of administration due to potential cardiovascular effects.
Medications to Avoid
- Blood Thinners:
- Warfarin: Co-administration may increase the risk of bleeding due to enhanced anticoagulant effects.
- Antiepileptic Drugs:
- Valproic Acid: There may be an increased risk of adverse effects when used together.
- Anxiolytics:
- Lorazepam: This medication can interact with nitazoxanide, potentially increasing sedation or other side effects.
- Anticonvulsants:
- Phenytoin: The interaction may affect the efficacy of both drugs.
- Other Medications:
- Baricitinib: Caution is advised when using this medication alongside nitazoxanide.
General Precautions
- Alcohol: Consumption should be avoided, as it may exacerbate side effects such as dizziness.
- Consultation: Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to ensure safe use of nitazoxanide.
Dosage of Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide is typically prescribed for the treatment of various parasitic infections and viral gastroenteritis. The standard dosage for adults and children over 12 years is:
- Adults and Children (12 years and older): 500 mg orally twice daily for 3 days.
- Children (1 to 11 years): The dosage is based on weight:
- 100 mg for those weighing 10 kg or less.
- 200 mg for those weighing between 11 kg and 25 kg.
- 500 mg for those weighing more than 25 kg, administered twice daily for 3 days.
It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Storage of Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide should be stored properly to maintain its effectiveness:
- Temperature: Store at room temperature, away from excessive heat and moisture (ideally between 20°C to 25°C or 68°F to 77°F).
- Container: Keep the medication in its original container, tightly closed, and out of reach of children.
- Expiration: Always check the expiration date before use, and do not use expired medications.
Reviews of Nitazoxanide
Patient reviews of nitazoxanide vary, reflecting individual experiences with the medication. Common themes in reviews include:
- Effectiveness: Many patients report positive outcomes, particularly in resolving gastrointestinal symptoms associated with infections.
- Side Effects: Some users experience mild side effects, such as nausea, abdominal pain, or headache. However, these are generally considered manageable.
- Convenience: The twice-daily dosing schedule for a short duration (3 days) is often appreciated by patients for its simplicity.
- Overall Satisfaction: Many patients express satisfaction with the medication’s ability to quickly alleviate symptoms, though experiences can vary based on individual health conditions.
Best Practices for Storing Medications
- Read Labels and Instructions:
- Always read the label or leaflet that comes with your medication for specific storage instructions. Some medications may require refrigeration, while others should be kept in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid Humid Areas:
- Do not store medications in the bathroom due to moisture and humidity from showers. Instead, opt for a dry, cool location like a closet or pantry.
- Keep Out of Reach of Children and Pets:
- Store medications in a high cabinet or a locked box to prevent accidental ingestion by children or pets. Ensure that all lids are tightly secured.
- Use Original Containers:
- Keep medications in their original containers to protect them from light and moisture. Original packaging is also helpful for identifying the medication and following dosage instructions.
- Check Expiration Dates Regularly:
- Review your medications every six to twelve months to discard any that are expired or no longer needed. Dispose of expired medications safely, preferably by returning them to a pharmacy.
- Avoid Combining Medications:
- Do not mix different medications in one container, as this can lead to confusion and potential adverse reactions. Each medication should be stored separately in its original packaging.
- Keep Away from Heat Sources:
- Store medications away from heat sources, such as above the stove or near the oven, as excessive heat can degrade the effectiveness of the medications.
- Remove Cotton from Bottles:
- If your medication bottle contains cotton, remove it immediately after opening. Cotton can absorb moisture, which may compromise the medication.
- Monitor for Changes:
- Be vigilant for any changes in the appearance, texture, or smell of medications, as these can indicate that they have gone bad.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.