GNC Folic Acid 1000mg 100’s Imported USA
GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg is a dietary supplement that provides 1000 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid per serving. It is a vegetarian formula imported from the USA and sold in 100-count bottles.The key benefits of GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg include:
- Supports healthy red blood cell production
- Assists in proper DNA formation
- Provides nutrients important for healthy fetal development
- Adequate folate intake is important for overall health
GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg is available for purchase on various online retail platforms, including Amazon, Vitamin Collection,
Original price was: ₨5,500.00.₨4,999.00Current price is: ₨4,999.00.
Out of stock
Description
GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg is a dietary supplement that provides 1000 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid per serving. It is a vegetarian formula imported from the USA and sold in 100-count bottles.The key benefits of GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg include:
- Supports healthy red blood cell production
- Assists in proper DNA formation
- Provides nutrients important for healthy fetal development
- Adequate folate intake is important for overall health
GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg is available for purchase on various online retail platforms, including Amazon, Vitamin Collection,
Product Overview
GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg is a dietary supplement that provides 1000 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid per serving. It is a vegetarian formula imported from the USA and sold in 100-count bottles.
Key Benefits of GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg
The key benefits of GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg include:
- Supports healthy red blood cell production
- Assists in proper DNA formation
- Provides nutrients important for healthy fetal development
- Adequate folate intake may help reduce a woman’s risk of having a child with a brain or spinal cord defect
Key Ingredients
Each GNC Folic Acid 1000mcg tablet contains:
- Folic Acid: 1000 mcg
- Calcium: 65 mg
How Folic Acid Supports DNA Formation
Folic acid, the synthetic form of the vitamin folate, plays a critical role in DNA synthesis and repair:Supports DNA Synthesis
- Folic acid is a coenzyme involved in the one-carbon transfer reactions necessary for the synthesis of DNA nucleotides (purines and pyrimidines) .
- It enables rapid cell division and growth by providing the building blocks for DNA in proliferating cells, such as those in the fetus, bone marrow, and trophoblastic tissue .
Assists DNA Repair
- Folic acid is required for the proper methylation of DNA, which is important for regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability .
- Adequate folic acid intake helps maintain the expression of DNA repair genes, which are important for fixing DNA damage and preventing mutations .
Prevents Birth Defects
- Folic acid supplementation during pregnancy has been shown to reduce the risk of neural tube defects and other congenital abnormalities by supporting proper DNA formation in the developing fetus .
Benefits of Folic Acid Supplementation for Pregnant Women
Folic acid supplementation provides numerous benefits for pregnant women and their developing babies:Prevents Neural Tube Defects
- Folic acid is crucial for the proper development of the baby’s brain and spinal cord, reducing the risk of neural tube defects like spina bifida and anencephaly by up to 70%.
- The CDC recommends all women of childbearing age take 400-800 mcg of folic acid daily, starting at least one month before pregnancy and continuing throughout pregnancy.
Lowers Risk of Congenital Heart Defects and Oral Clefts
- Periconceptional folic acid supplementation may also prevent congenital heart disease and oral clefts in babies.
Supports Red Blood Cell Production
- Folic acid is essential for the production of red blood cells, preventing folate-deficiency anemia which can impair oxygen transport and organ function.
Reduces Risk of Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight
- Some studies suggest folic acid supplementation may lower the risk of preterm birth and having a baby with low birth weight.
Potential Benefits for Fertility and Pregnancy Loss
- Research indicates folic acid may enhance fertility and reduce pregnancy loss, though more studies are needed.
Mechanism of Action of Folic Acid
Folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, plays a crucial role in several biological processes, including DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and fetal development. Here are the key mechanisms of action:
- DNA Synthesis and Repair:
- Folic acid is a coenzyme involved in one-carbon transfer reactions necessary for the synthesis of DNA nucleotides (purines and pyrimidines).
- It helps in the replication and repair of DNA, ensuring genomic stability and preventing mutations.
- Red Blood Cell Production:
- Folic acid is essential for the production of red blood cells, preventing folate-deficiency anemia by ensuring proper hemoglobin synthesis.
- Fetal Development:
- Folic acid supports healthy fetal development by providing nutrients critical for brain and spinal cord formation.
- Adequate folic acid intake during pregnancy reduces the risk of neural tube defects and other congenital abnormalities.
- Homocysteine Regulation:
- Folic acid helps maintain normal homocysteine levels, which is important for cardiovascular health and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Can Folic Acid Supplements Improve Energy Levels?
While folic acid is essential for energy production, there is limited evidence that folic acid supplements alone can significantly boost energy levels in people without a deficiency:
- Folic acid is one of the B-complex vitamins that help convert food into fuel (glucose) to produce energy.
- Folate deficiency, which is fairly common, can lead to anemia and fatigue. Correcting a deficiency with folic acid supplements may help restore energy levels in these cases.
- However, for individuals who are not deficient, folic acid supplementation is unlikely to provide a noticeable boost in energy or reduce tiredness and fatigue.
- Other nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and vitamin C are more directly involved in energy metabolism and may have a greater impact on energy levels when supplemented.
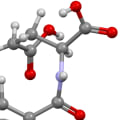 FolateVitamin B9MoreDefinitionA B vitamin essential for DNA and RNA synthesis, cell division, and amino acid metabolism.Dietary ImportanceCannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through diet.FormsOccurs naturally in food and as manufactured folic acid; folic acid is converted to folate in the body.
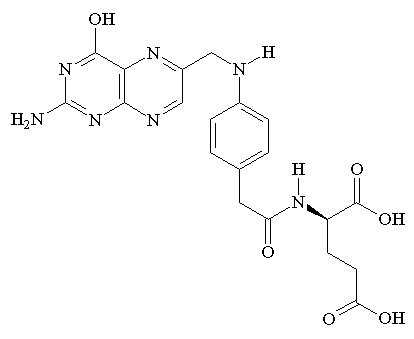
FolateVitamin B9MoreDefinitionA B vitamin essential for DNA and RNA synthesis, cell division, and amino acid metabolism.Dietary ImportanceCannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through diet.FormsOccurs naturally in food and as manufactured folic acid; folic acid is converted to folate in the body.Chemical Structure of Folic Acid
Folic acid consists of three main moieties:
- The pterin (or pteridine) ring
- Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is conjugated to the pterin ring by a methylene bridge
- Glutamic acid, which is attached to PABA
The full chemical structure of folic acid is:N-(4-{[(2-Amino-4-hydroxy-6-pteridinyl)methyl]amino}benzoyl)glutamic acidThe molecular formula is C19H19N7O6 and the IUPAC name is pteroyl-L-glutamic acid.The chemical structure can be represented as:c1cc(ccc1C(=O)NC@@HC(=O)O)NCc2cnc3c(n2)c(nc(n3)N)O

Dosage
The recommended dosages for folic acid supplements are:Adults
- Megaloblastic anemia: 1 mg daily
- Folic acid deficiency: 400 mcg daily
- Pregnancy/lactation: 600-800 mcg daily
Children
- 0-6 months: 65 mcg daily
- 1-3 years: 150 mcg daily
- 4-8 years: 200 mcg daily
- 9-13 years: 300 mcg daily
- 14+ years: 400 mcg daily
Higher doses up to 4-5 mg daily may be prescribed for certain conditions like neural tube defect prevention.
Storage
Folic acid supplements should be stored:
- At room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light
- In a tightly closed container
- Avoid freezing
Reviews
Folic acid supplements are generally well-tolerated, with few reported side effects. Common reviews include:
- “I’ve been taking this folic acid supplement for years and it has helped maintain my energy levels.”
- “This folic acid is easy to take and has supported my pregnancy so far.”
- “No issues with this folic acid – it’s an affordable way to get the recommended daily amount.”
- “Folic acid is an essential nutrient, and this supplement has been great for keeping my levels in a healthy range.”
Precautions for Taking Folic Acid Supplements
Based on the search results, here are the key precautions to consider when taking folic acid supplements:Avoid in Certain Medical Conditions
- Folic acid should not be used for the treatment of pernicious anemia or undiagnosed megaloblastic anemia without sufficient vitamin B12, as it may mask the B12 deficiency.
- Caution should be exercised when administering folic acid to patients who may have folate-dependent tumors.
Interactions with Medications
- Folic acid may interact with certain medications, including:
- Sulfasalazine (may reduce absorption of folic acid)
- Cholestyramine (may interfere with folic acid absorption)
- Antibiotics (may interfere with folic acid assays)
- Trimethoprim or sulfonamides (may reduce the effect of folic acid)
- Anticonvulsant drugs (may reduce serum levels)
- Fluorouracil (may increase toxicity)
- Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium (may reduce folic acid absorption)
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Folic acid is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but very high doses have been shown to cause fetal abnormalities in animal studies.
- Folic acid is excreted in breast milk, but no adverse effects have been observed in breastfed infants.
Other Precautions
- Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take folic acid supplements.
- Folic acid is removed by hemodialysis, so dosage may need to be adjusted for patients undergoing dialysis.
Common Dietary Restrictions
Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
- Vegetarians avoid meat, poultry, and fish, but may consume dairy and eggs.
- Vegans avoid all animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs.
Lactose Intolerance
- Caused by a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose (milk sugar).
- Leads to digestive issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming dairy products.
- Can often tolerate small amounts of lactose or low-lactose dairy products.
Gluten Intolerance
- Includes celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
- Requires avoidance of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Religious Dietary Restrictions
- Kosher – Jewish dietary laws with restrictions on certain foods and preparation methods.
- Halal – Islamic dietary standards with rules around animal slaughter and prohibited foods like pork.
Other Common Restrictions
- Diabetes – Focuses on moderate carb intake, high fiber, and low-GI foods.
- Dairy-free – Avoids all dairy products, including milk, cheese, and butter.
- Keto diet – Very low in carbs, high in fats, moderate protein.
- DNA Synthesis and Repair:








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.