Xanax alprazolaam 0.5mg 30’ct tablets in Pakistan
Xanax (Alprazolam) 0.5 mg in Pakistan
Overview
- Generic Name: Alprazolam
- Brand Name: Xanax
- Dosage: 0.5 mg
- Packaging: Typically available in packs of 30 tablets.
Indications
- Primary Uses:
- Treatment of anxiety disorders
- Management of panic disorders
- Sometimes prescribed for anxiety associated with depression
Mechanism of Action
- How It Works: Alprazolam enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.
Prescription and Availability
- Prescription Requirement:
- Xanax is classified as a controlled substance in Pakistan.
- It can only be obtained with a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider.
Risks and Precautions
- Potential for Misuse:
- Xanax can lead to addiction and dependence if misused.
- Abrupt discontinuation can result in withdrawal symptoms.
- Common Side Effects:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Potential respiratory depression, especially when combined with other depressants (e.g., alcohol, opioids).
-
-
Original price was: ₨5,500.00.₨4,999.00Current price is: ₨4,999.00.
Description
Xanax (Alprazolam) 0.5 mg in Pakistan
Overview
- Generic Name: Alprazolam
- Brand Name: Xanax
- Dosage: 0.5 mg
- Packaging: Typically available in packs of 30 tablets.
Indications
- Primary Uses:
- Treatment of anxiety disorders
- Management of panic disorders
- Sometimes prescribed for anxiety associated with depression
Mechanism of Action
- How It Works: Alprazolam enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.
Prescription and Availability
- Prescription Requirement:
- Xanax is classified as a controlled substance in Pakistan.
- It can only be obtained with a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider.
Risks and Precautions
- Potential for Misuse:
- Xanax can lead to addiction and dependence if misused.
- Abrupt discontinuation can result in withdrawal symptoms.
- Common Side Effects:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Potential respiratory depression, especially when combined with other depressants (e.g., alcohol, opioids).
Key Benefits of Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Effective Anxiety Relief: Xanax is primarily used to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder. Clinical studies have shown that it significantly reduces anxiety symptoms compared to placebo, as measured by various psychometric scales.
- Rapid Onset of Action: The medication typically begins to work within 15 to 45 minutes, providing quick relief from anxiety and panic symptoms.
- Improvement in Panic Attacks: Xanax has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the frequency of panic attacks, with studies indicating that a significant percentage of patients experience a reduction in panic episodes while on the medication.
- Versatile Dosage Forms: Available in various strengths (0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, and 2 mg), Xanax can be tailored to individual patient needs, allowing for flexible dosing based on the severity of symptoms.
- Short-term Use for Acute Situations: Xanax can be beneficial for short-term management of anxiety in stressful situations, making it a useful option for patients needing immediate relief.
Key Ingredients
- Active Ingredient:
- Alprazolam: The primary active ingredient in Xanax, which is a benzodiazepine. It works by enhancing the activity of neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which has a calming effect on the nervous system.
- Inactive Ingredients:
- Xanax tablets may contain various inactive ingredients such as lactose, starch, and coloring agents, which can vary by manufacturer and formulation. Specific formulations may differ based on the tablet strength and type (e.g., extended-release) but are generally designed to aid in the drug’s absorption and stability.
 AlprazolamPotent tranquilizer used in anxiety disorder managementMorePrimary useManagement of anxiety disorders, specifically panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nauseaCommon side effectsSleepiness, depression, impaired motor skills and cognition, dry mouth, decreased heart rate, and in higher doses, impairment of judgment and memory lossWithdrawal riskVery high, with risk of withdrawal symptoms if use is suddenly decreasedXanax (alprazolam) is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter in the brain that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.Specifically, alprazolam binds to specific receptors on GABA-A receptors, which allows more chloride ions to enter the neuron. This makes the neuron less responsive to excitatory neurotransmitters, resulting in a calming effect on the nervous system.The exact mechanism of action is not fully known, but clinically, all benzodiazepines cause a dose-related central nervous system depressant activity. Alprazolam exerts its effect for the acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder.
AlprazolamPotent tranquilizer used in anxiety disorder managementMorePrimary useManagement of anxiety disorders, specifically panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nauseaCommon side effectsSleepiness, depression, impaired motor skills and cognition, dry mouth, decreased heart rate, and in higher doses, impairment of judgment and memory lossWithdrawal riskVery high, with risk of withdrawal symptoms if use is suddenly decreasedXanax (alprazolam) is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter in the brain that promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety.Specifically, alprazolam binds to specific receptors on GABA-A receptors, which allows more chloride ions to enter the neuron. This makes the neuron less responsive to excitatory neurotransmitters, resulting in a calming effect on the nervous system.The exact mechanism of action is not fully known, but clinically, all benzodiazepines cause a dose-related central nervous system depressant activity. Alprazolam exerts its effect for the acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder.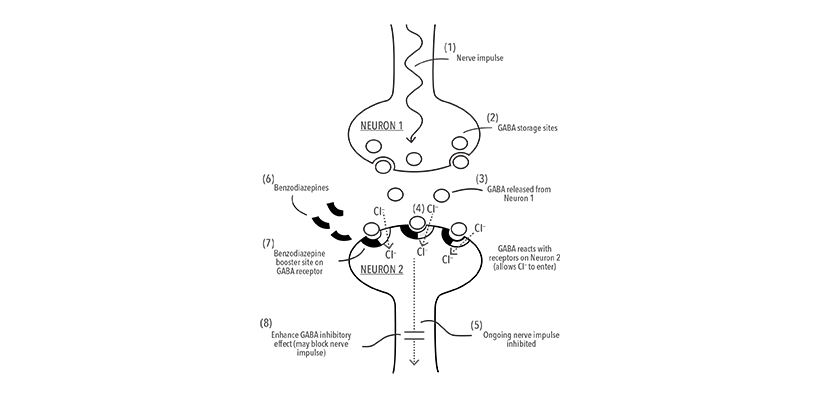
Key Precautions for Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Medical History Disclosure: Before starting Xanax, inform your healthcare provider about your complete medical history, especially if you have conditions such as:
- Glaucoma
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Lung disease (e.g., COPD)
- History of substance use disorder
- Age Considerations: Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of Xanax, increasing the risk of side effects like drowsiness and loss of coordination. A lower dose may be necessary.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Xanax can harm an unborn baby and may cause withdrawal symptoms in newborns if taken late in pregnancy. It is not recommended during breastfeeding as it can pass into breast milk.
- Driving and Operating Machinery: Xanax can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until you know how the medication affects you.
- Alcohol and Drug Interactions: Avoid consuming alcohol while taking Xanax, as it can significantly increase the risk of serious side effects, including respiratory depression and sedation. Be cautious with other CNS depressants.
- Dosage Management: Do not exceed the prescribed dosage, as misuse can lead to addiction, overdose, and serious side effects. Gradually reduce the dosage under medical supervision if discontinuing.
- Surgery Notification: Inform your healthcare providers about your Xanax use before any surgical procedures, including dental surgery.
Dietary Restrictions
- Grapefruit Products: Avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking Xanax, as they can increase the risk of side effects by affecting the metabolism of the drug.
- Cannabis: Using cannabis alongside Xanax can enhance the sedative effects, increasing the risk of side effects such as excessive drowsiness and impaired coordination.
- Herbal Supplements: Be cautious with herbal supplements like St. John’s Wort, which may reduce the effectiveness of Xanax. Always consult your doctor before combining Xanax with any supplements.
Foods to Avoid
- Grapefruit and Grapefruit Juice:
- Grapefruit products can interfere with the metabolism of Xanax in the body. They inhibit the enzyme CYP3A4, which is responsible for breaking down alprazolam. This can lead to increased levels of the medication in your system, heightening the risk of side effects such as drowsiness and respiratory depression.
- Alcohol:
- Alcohol should be completely avoided while taking Xanax. The combination can amplify the sedative effects of both substances, leading to severe drowsiness, respiratory depression, decreased awareness, and even coma in extreme cases. This combination can be life-threatening.
- Cannabis:
- Using cannabis products alongside Xanax can increase the sedative effects, which may lead to excessive sleepiness and impaired cognitive function. Caution is advised if considering the use of cannabis while on Xanax.
- Herbal Supplements:
- Certain herbal supplements, particularly St. John’s Wort, should be avoided as they can speed up the metabolism of Xanax, potentially reducing its effectiveness. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements while on Xanax.
Drug Interactions
- CNS Depressants:
- Alcohol: Combining Xanax with alcohol can lead to severe sedation, respiratory depression, and increased risk of overdose. It is advised to avoid alcohol entirely while taking Xanax.
- Opioids: Concurrent use can increase the risk of respiratory depression and sedation, potentially leading to fatal outcomes. Close monitoring is required if these are used together.
- Antifungals:
- Ketoconazole and Itraconazole: These strong CYP3A inhibitors can significantly increase the levels of Xanax in the body, raising the risk of side effects. Caution is advised, and dosage adjustments may be necessary.
- Antibiotics:
- Clarithromycin and Erythromycin: These can also inhibit the metabolism of Xanax, leading to increased drug levels and potential toxicity.
- Other Medications:
- Nefazodone, Fluvoxamine, and Cimetidine: These drugs can inhibit the metabolism of Xanax, necessitating caution and possible dosage adjustments.
- Sleep Aids:
- Valerian and Melatonin: Taking these with Xanax can enhance sedation and increase the risk of excessive drowsiness.
- St. John’s Wort:
- This herbal supplement can decrease the effectiveness of Xanax by speeding up its metabolism, potentially leading to inadequate treatment of anxiety.
Food Interactions
- Grapefruit and Grapefruit Juice:
- Grapefruit products can inhibit the enzyme CYP3A4, which is responsible for metabolizing Xanax. This can lead to increased levels of the drug in the body, raising the risk of side effects. It is recommended to avoid grapefruit while taking Xanax.
Common Medications That Interact with Xanax
- CNS Depressants:
- Opioids (e.g., morphine, fentanyl): Combining these can significantly increase the risk of respiratory depression and sedation, leading to potentially fatal outcomes.
- Antidepressants:
- Amitriptyline
- Mirtazapine
- Trazodone
- Antipsychotics:
- Haloperidol
- Risperidone
- Seizure Medications:
- Gabapentin
- Topiramate
- Muscle Relaxants:
- Carisoprodol
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Sleeping Pills:
- Zaleplon
- Zolpidem
- Sedating Antihistamines:
- Chlorpheniramine
- Promethazine
- Antifungal Medications:
- Ketoconazole
- Itraconazole: These drugs inhibit the metabolism of Xanax, leading to increased drug levels and a higher risk of side effects.
- Antibiotics:
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin: Similar to antifungals, these antibiotics can prevent the breakdown of Xanax, increasing its concentration in the body.
- Other Medications:
- Nefazodone and Fluvoxamine: Both can inhibit the metabolism of Xanax, necessitating caution and possible dosage adjustments.
- Cimetidine: This medication can also affect Xanax metabolism.
- Herbal Supplements:
- St. John’s Wort: This supplement can decrease the effectiveness of Xanax by speeding up its metabolism.
Use During Pregnancy
Risks to the Fetus
- Pregnancy Category: Xanax is classified as a Category D medication by the FDA, indicating that there is evidence of risk to the fetus. It is associated with potential congenital malformations, especially when taken during the first trimester, which can increase the risk of birth defects such as cleft lip and palate.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Use of Xanax in the later stages of pregnancy may lead to withdrawal symptoms in newborns, including irritability, feeding difficulties, and respiratory issues. This condition is sometimes referred to as “floppy infant syndrome,” where infants may exhibit weak muscle tone and difficulty controlling their movements.
- Long-term Effects: There are concerns about possible long-term developmental issues in children exposed to benzodiazepines in utero, although more research is needed to fully understand these effects.
Recommendations
- Consultation Required: Pregnant women currently taking Xanax or considering its use should consult their healthcare provider to weigh the potential risks and benefits. In many cases, healthcare providers may recommend discontinuing the medication or exploring safer alternatives for managing anxiety during pregnancy.
Use During Breastfeeding
Risks to the Infant
- Excretion in Breast Milk: Xanax is excreted in breast milk, and while the exact effects on breastfeeding infants are not fully understood, there have been reports of sedation and poor feeding in infants exposed to the drug through breast milk.
- Recommendations Against Use: Due to the potential for serious side effects in infants, including sedation and withdrawal symptoms, it is generally recommended that breastfeeding mothers avoid using Xanax. If a mother must take Xanax, a decision should be made to either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue the medication, based on a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider.
Risks to the Infant
- Transfer to Breast Milk:
- Xanax can be secreted in trace amounts into breast milk, which means that infants can ingest small quantities of the drug. This transfer can lead to adverse effects in newborns, as their bodies are more sensitive to medications.
- Potential Side Effects:
- Infants exposed to Xanax through breast milk may experience symptoms such as:
- Drowsiness or excessive sleepiness
- Increased irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Weight loss
- Agitation and restlessness
- These effects can be particularly concerning for newborns and premature babies, who may be more vulnerable to the sedative effects of the drug.
- Infants exposed to Xanax through breast milk may experience symptoms such as:
- Withdrawal Symptoms:
- Prolonged exposure to Xanax through breastfeeding may lead to dependency in infants, resulting in withdrawal symptoms if breastfeeding is stopped suddenly. Symptoms can include increased crying, irritability, and poor sleep patterns.
Risks to the Mother
- Side Effects of Xanax:
- Mothers taking Xanax may experience side effects such as:
- Excessive drowsiness
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
- Behavioral changes
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and headaches
- These side effects can impair the mother’s ability to care for her infant safely.
- Mothers taking Xanax may experience side effects such as:
- Impact on Breastfeeding:
- The sedative effects of Xanax can affect a mother’s ability to breastfeed effectively. Drowsiness or confusion can hinder her responsiveness to the baby’s needs, potentially impacting feeding schedules and the overall mother-infant bond.
- Increased Prolactin Levels:
- Xanax may increase prolactin levels, which can enhance milk production but may also lead to complications such as galactorrhea (milky discharge from the nipples) and hormonal imbalances that affect mood and overall health.
Xanax Dosage
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Starting Dosage: 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg three times daily
- Maximum Dosage: 4 mg per day, split into three doses
- Dosage Adjustments: Every 3-4 days based on response
Panic Disorder
- Starting Dosage: 0.5 mg three times daily
- Average Dosage: 5-6 mg per day, split into three doses
- Maximum Dosage: 10 mg per day, split into three doses
- Dosage Adjustments: Every 3-4 days, no more than 1 mg per day increase
Storage
- Store at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F)
- Keep in a tightly sealed container, away from light and moisture
- Avoid storing in bathrooms due to potential dampness
- Keep out of reach of children and pets
Disposal
- Dispose of unused medication properly to avoid accidental ingestion
- Check with your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for guidelines
User Reviews
“Xanax has been a lifesaver for my anxiety. It helps me feel calm and in control during stressful situations.””I’ve been taking Xanax for years and it still works well for me. The key is sticking to the prescribed dosage.””Xanax works quickly to relieve my panic attacks. However, I’ve noticed I need to take higher doses over time to get the same effect.””Xanax makes me feel very sleepy and groggy the next day. I try to only take it when absolutely necessary.””I had a bad experience with Xanax. It made me act aggressively and do things I normally wouldn’t do. I stopped taking it immediately.”






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.