Kayexalate Powder 454’gm
Medication Overview
Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) is a medication used to treat high levels of potassium in the blood, known as hyperkalemia. It works by helping the body eliminate excess potassium.
Dosage and Administration
- Oral: 15-60g per day, given as 15g (4 teaspoons) 1-4 times daily
- Rectal: 30-50g every 6 hours
- The powder should be mixed with water or syrup and taken immediately. For rectal use, it is given as an enema after a cleansing enema, and retained for as long as possible before flushing.
Product Details
- Comes as a cream to light brown powder in 454g jars
- Should be stored at 15-30°C
Potential Side Effects
- Intestinal necrosis, electrolyte disturbances, aspiration, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, metabolic alkalosis
- May interact with other oral medications
-
Original price was: ₨15,000.00.₨13,999.00Current price is: ₨13,999.00.
Description
Medication Overview
Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) is a medication used to treat high levels of potassium in the blood, known as hyperkalemia. It works by helping the body eliminate excess potassium.
Dosage and Administration
- Oral: 15-60g per day, given as 15g (4 teaspoons) 1-4 times daily
- Rectal: 30-50g every 6 hours
- The powder should be mixed with water or syrup and taken immediately. For rectal use, it is given as an enema after a cleansing enema, and retained for as long as possible before flushing.
Product Details
- Comes as a cream to light brown powder in 454g jars
- Should be stored at 15-30°C
Potential Side Effects
- Intestinal necrosis, electrolyte disturbances, aspiration, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, metabolic alkalosis
- May interact with other oral medications
Key Benefits of Kayexalate Powder
- Treats high levels of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia) by helping the body eliminate excess potassium
- Lowers potassium levels in the blood by binding to potassium in the intestine
Key Ingredient
- The active ingredient is sodium polystyrene sulfonate powder
Kayexalate powder contains sodium polystyrene sulfonate as the sole active ingredient. It works by exchanging sodium ions for potassium ions in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing the body to excrete the excess potassium in the stool. This helps lower dangerously high potassium levels in the blood.

- Binding to Other Medications:
- Kayexalate can bind to other orally administered medications, which may decrease their gastrointestinal absorption and lead to reduced efficacy. This interaction is more significant when Kayexalate is taken close to other medications. Patients should take other oral medications at least 3 hours before or 3 hours after Kayexalate, especially those with gastroparesis, who may require a 6-hour separation.
- Cation-Donating Antacids:
- The simultaneous use of Kayexalate with nonabsorbable cation-donating antacids and laxatives may reduce the resin’s potassium exchange capability and increase the risk of systemic alkalosis. Magnesium-containing laxatives should not be used with Kayexalate.
- Sorbitol:
- The concomitant use of sorbitol, a sugar-free sweetener, with Kayexalate may contribute to the risk of intestinal necrosis and is not recommended.
- Specific Medications:
- Kayexalate interacts with several medications, including:
- Digoxin
- Laxatives such as magnesium hydroxide or aluminum carbonate
- Thyroxine
- Lithium
- Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium
- Sorbitol
- Immunosuppressant drugs.
- Kayexalate interacts with several medications, including:
-
Mechanism of Action
Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) works by exchanging sodium ions for potassium ions in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing the body to excrete the excess potassium in the stool. This helps lower dangerously high potassium levels in the blood.Specifically, Kayexalate:
- Is a non-absorbed, cation exchange polymer that contains a sodium counterion
- Increases fecal potassium excretion through binding of potassium in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract
- Binding of potassium reduces the concentration of free potassium in the gastrointestinal lumen, resulting in a reduction of serum potassium levels
- As the resin passes along the intestine or is retained in the colon, the sodium ions are partially released and are replaced by potassium ions, primarily in the large intestine
The practical exchange ratio is 1 mEq K per 1 gram of resin. However, the efficiency of this process is limited and unpredictably variable, with an in vivo efficiency of approximately 33 percent.

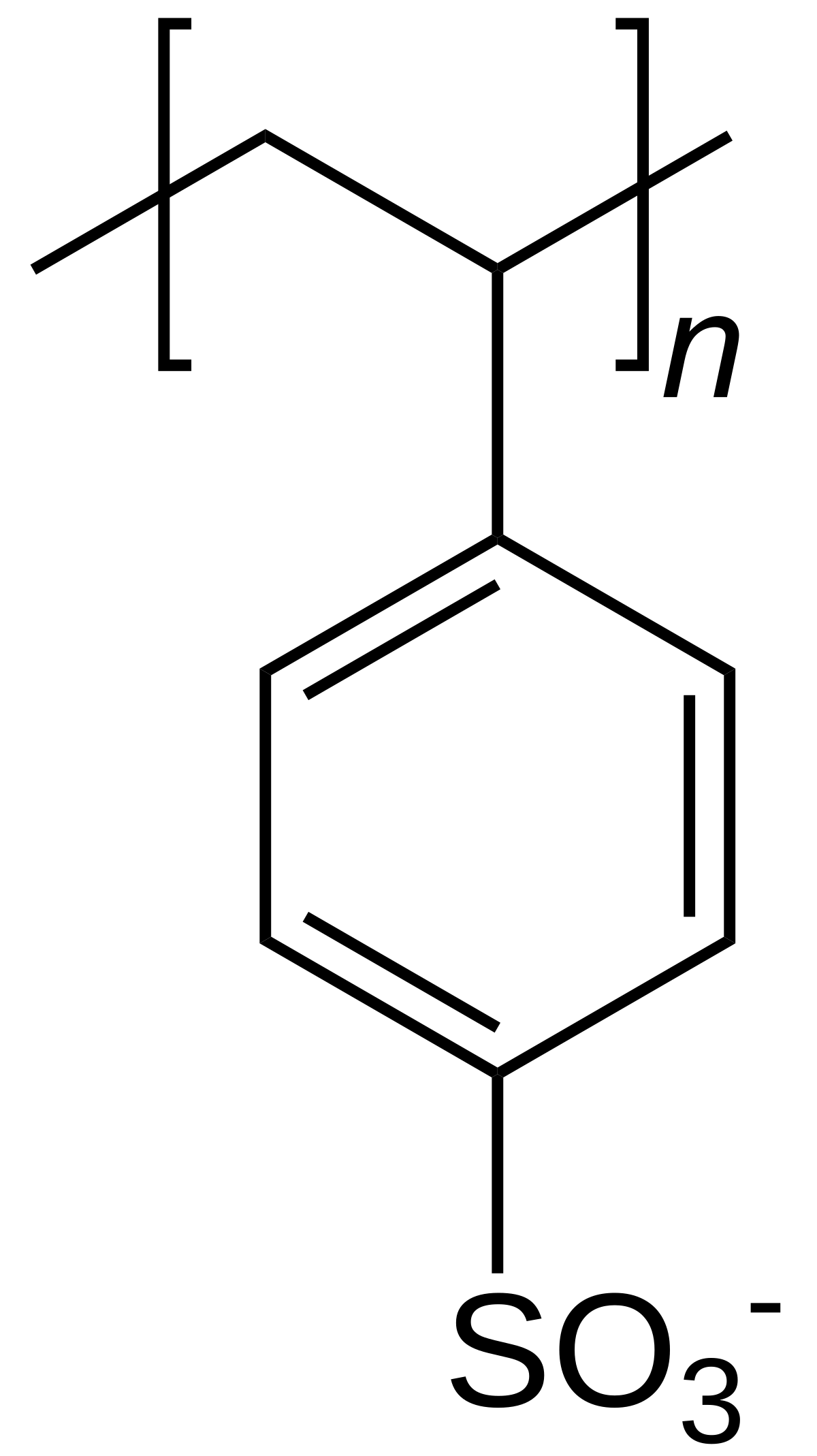
 Polystyrene sulfonateMedication group for treating high blood potassiumMorePrimary useTreats high blood potassium levels and removes potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical applicationsCommon side effectsLoss of appetite, gastrointestinal upset, constipation, and low blood calciumForms suppliedSupplied in sodium or calcium form; used as a potassium binder in kidney disease treatmentsKayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) has the following chemical structure:Kayexalate chemical structureThe key structural features are:
Polystyrene sulfonateMedication group for treating high blood potassiumMorePrimary useTreats high blood potassium levels and removes potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in technical applicationsCommon side effectsLoss of appetite, gastrointestinal upset, constipation, and low blood calciumForms suppliedSupplied in sodium or calcium form; used as a potassium binder in kidney disease treatmentsKayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) has the following chemical structure:Kayexalate chemical structureThe key structural features are:- It is a cation-exchange resin composed of a polystyrene backbone with sulfonate groups attached
- The sulfonate groups are the active sites that bind potassium ions
- The sodium counterion is exchanged for potassium in the gastrointestinal tract
- The polymer structure allows the resin to pass through the GI tract while binding potassium
The molecular formula is C8H7CaO3S+ and the molecular weight is 223.28 g/mol. The calcium salt is used in the oral formulation.
Key Precautions
Intestinal Necrosis
- Cases of intestinal necrosis, some fatal, and other serious gastrointestinal events (bleeding, ischemic colitis, perforation) have been reported with Kayexalate use.
Electrolyte Disturbances
- Kayexalate can cause severe electrolyte disturbances like hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia. Close monitoring of electrolytes is required.
Fluid Overload
- Patients sensitive to high sodium intake may experience fluid overload. Monitor for signs of fluid overload.
Aspiration Risk
- Acute bronchitis or bronchopneumonia has been reported due to inhalation of Kayexalate particles, especially in neonates.
Binding to Other Medications
- Kayexalate can bind to other orally administered medications, decreasing their absorption. Take other medications at least 3 hours before or after Kayexalate.
Concomitant Use of Sorbitol
- Concomitant use of sorbitol with Kayexalate may contribute to the risk of intestinal necrosis and is not recommended.
Dietary Restrictions with Kayexalate
When taking Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate), there are a few key dietary restrictions to be aware of:
- Avoid Potassium-Rich Foods:
- Kayexalate works by binding to potassium in the gastrointestinal tract, so it’s important to avoid foods high in potassium. This includes:
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Bananas
- Tomatoes
- Potatoes
- Beans
- Nuts
- Whole grains
- Kayexalate works by binding to potassium in the gastrointestinal tract, so it’s important to avoid foods high in potassium. This includes:
- Avoid Mixing with Fruit Juices:
- Do not mix Kayexalate powder with orange juice or other fruit juices, as they contain high amounts of potassium.
- Limit Sodium Intake:
- Kayexalate contains sodium, so patients sensitive to sodium may need to restrict their overall sodium intake from other dietary sources.
- Avoid Magnesium-Containing Laxatives:
- Magnesium-containing laxatives, such as magnesium hydroxide or magnesium citrate, should not be used with Kayexalate as they can interact and reduce the effectiveness of the medication.
- Increase Fiber Intake:
- To help prevent constipation, which is a common side effect of Kayexalate, it’s recommended to increase dietary fiber intake through foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Dosage
The typical adult dosage for Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) is:Oral Administration:
- 15-60g per day, given as 15g (4 teaspoons) 1-4 times daily
Rectal Administration:
- 30-50g every 6 hours
The powder should be mixed with water or syrup and taken immediately. For rectal use, it is given as an enema after a cleansing enema, and retained for as long as possible before flushing.
Storage
Kayexalate comes as a cream to light brown powder available in 454g jars. It should be stored at 15-30°C (59-86°F).The suspension should be freshly prepared and used within 24 hours. The powder should not be heated, as this could alter the exchange properties of the resin.
Reviews
Kayexalate is generally well-tolerated, but can cause some side effects:
- Gastrointestinal: Constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, intestinal necrosis
- Metabolic: Electrolyte disturbances like hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, metabolic alkalosis
- Respiratory: Aspiration, especially in neonates
Use in Pediatric Patients
- Studies of the safety and efficacy of Kayexalate have not been specifically conducted in pediatric patients.
- However, in pediatric patients, as in adults, Kayexalate is expected to bind potassium at the practical exchange ratio of 1 mEq potassium per 1 gram of resin.
Precautions in Pediatric Use
- In neonates, Kayexalate should not be given by the oral route, as it may result in impaction of the resin.
- In both children and neonates, excessive dosage or inadequate dilution of Kayexalate could also result in impaction.
- Premature infants or low birth weight infants may have an increased risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects with Kayexalate use.
Monitoring Requirements
- Close monitoring is required when using Kayexalate in pediatric patients, especially neonates and premature/low birth weight infants.
- Careful attention must be paid to the dose, dilution, and administration route to avoid complications like impaction or gastrointestinal adverse events.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.