Ocrevus Ocrelizumab 300mg 10ml Injection In Pakistan
Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) 300mg/10ml Injection in Pakistan
Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) 300mg/10ml injection is available in Pakistan for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) and primary progressive MS in adults.
Key Details
- Each vial contains 300 mg of ocrelizumab in 10 mL at a concentration of 30 mg/mL
- The initial 600 mg dose is administered as two separate 300 mg infusions, followed by a single 600 mg infusion every 6 months
- Premedication with methylprednisolone, an antihistamine, and an antipyretic is required to reduce infusion-related reactions
- The price range in Pakistan is Rs. 450,000 to Rs. 520,000 per vial
Ocrevus is the first approved treatment for primary progressive MS and has been approved by major regulatory agencies including the FDA, EMA, Health Canada, TGA, and Medsafe.
Original price was: ₨60,000.00.₨55,000.00Current price is: ₨55,000.00.
Description
Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) 300mg/10ml Injection in Pakistan
Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) 300mg/10ml injection is available in Pakistan for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) and primary progressive MS in adults.
Key Details
- Each vial contains 300 mg of ocrelizumab in 10 mL at a concentration of 30 mg/mL
- The initial 600 mg dose is administered as two separate 300 mg infusions, followed by a single 600 mg infusion every 6 months
- Premedication with methylprednisolone, an antihistamine, and an antipyretic is required to reduce infusion-related reactions
- The price range in Pakistan is Rs. 450,000 to Rs. 520,000 per vial
Ocrevus is the first approved treatment for primary progressive MS and has been approved by major regulatory agencies including the FDA, EMA, Health Canada, TGA, and Medsafe.
Key Benefits of Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) 300mg/10ml Injection
- Significantly reduces the number of attacks (relapses) in relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (RMS) and delays the worsening of the disease
- Increases the chances that a patient will not experience any signs of disease activity (changes in the brain, relapse and deterioration of functional capacity) in RMS
- Slows the progression of primary progressive MS (PPMS) and limits the deterioration of walking speed
- Reduces inflammation and the attack on the myelin sheath, which helps protect nerve cells
Key Ingredients
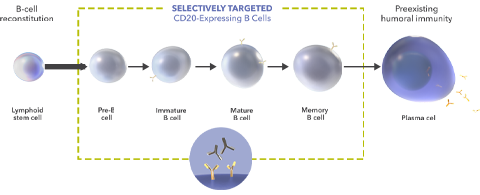
Ocrevus contains the active ingredient ocrelizumab, which is a humanized monoclonal antibody produced by recombinant DNA technology. Each 10 mL vial contains 300 mg of ocrelizumab at a concentration of 30 mg/mL.Ocrelizumab works by targeting CD20-positive B cells, leading to their depletion. B cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a role in the immune system’s attack on the myelin sheath in multiple sclerosis. By removing these specific B cells, ocrelizumab helps reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.
Combination with Other Medications
Interactions with Corticosteroids
Ocrevus can interact with corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone, methylprednisolone), which are often used to treat inflammation. Using them together may increase the risk of infections due to the immunosuppressive effects of both drugs.
Immunosuppressive Therapies
Combining Ocrevus with other immunosuppressive or immune-modulating therapies (e.g., fingolimod, natalizumab) is also discouraged. This combination can further elevate the risk of infections and may enhance the immunosuppressive effects.
Vaccinations
Live vaccines are not recommended during Ocrevus treatment and until B-cell repletion occurs, as Ocrevus can decrease the effectiveness of these vaccines and increase the risk of infections. It is generally recommended to avoid certain medications when taking Ocrevus (ocrelizumab) due to the potential for increased risks, particularly infections. Some key interactions to be aware of include:
Corticosteroids
Ocrevus can interact with corticosteroids (e.g. dexamethasone, methylprednisolone, prednisone) used to treat inflammation. Taking them together may increase the risk of infections due to the immunosuppressive effects of both drugs.
Immunosuppressive Therapies
Combining Ocrevus with other immunosuppressive or immune-modulating therapies (e.g. fingolimod, natalizumab, teriflunomide, mitoxantrone) is discouraged as it can further elevate the risk of infections and may enhance immunosuppression.
Vaccinations
Live vaccines should not be given during Ocrevus treatment and until B-cell repletion occurs, as Ocrevus can decrease the effectiveness of these vaccines and increase the risk of infections.Before starting Ocrevus, patients should inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to manage potential interactions effectively. Close monitoring for infections is recommended when combining Ocrevus with other immunosuppressants.
Mechanism of Action
Ocrevus is a humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically targets CD20-positive B cells, a type of immune cell that plays a crucial role in the inflammatory processes associated with MS. Here’s how it works:
- Targeting CD20-Positive B Cells: Ocrelizumab binds to the CD20 protein found on the surface of B cells. This protein is not present on all B cells, allowing for selective targeting without completely depleting the immune system’s ability to fight infections.
- Depletion of B Cells: By binding to CD20, Ocrevus marks these B cells for destruction by the immune system. This leads to a significant reduction in the population of these cells, which are implicated in the autoimmune attack on myelin, the protective sheath around nerve fibers.
- Reduction of Inflammation: The depletion of CD20-positive B cells reduces the inflammatory response in the central nervous system (CNS). This is crucial in mitigating the damage to myelin and nerve cells, thereby slowing disease progression and reducing the frequency of relapses in relapsing forms of MS.
- Impact on Disease Activity: Clinical trials have shown that Ocrevus significantly decreases the annualized relapse rate and delays the progression of disability in patients with both relapsing and primary progressive forms of MS. It also reduces the number of lesions observed on MRI scans, indicating a decrease in disease activity.
Ocrelizumab, the active ingredient in Ocrevus, is a humanized monoclonal antibody with a specific chemical structure that allows it to target CD20-positive B cells. While the exact chemical structure is not detailed in the search results, it can be summarized as follows:
Chemical Structure of Ocrelizumab
- Type: Monoclonal antibody
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 145 kDa
- Structure: Ocrelizumab consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains, forming a Y-shaped structure typical of antibodies. The heavy chains contain constant and variable regions, which are crucial for binding to the CD20 antigen on B cells.
Functional Groups
The structure includes various functional groups typical of proteins, such as:
- Amino Acids: Comprised of 2,000+ amino acids, which form the polypeptide chains.
- Glycosylation Sites: Ocrelizumab is glycosylated, meaning it has carbohydrate groups attached, which are important for its stability and activity.
Mechanism of Action
Ocrelizumab binds specifically to CD20, leading to the depletion of B cells through mechanisms such as:
- Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
These interactions reduce inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath in multiple sclerosis.

Key Precautions for Ocrevus (ocrelizumab)
When using Ocrevus, several precautions should be considered to ensure patient safety and effectiveness of the treatment:
Infusion Reactions
- Monitoring Required: Patients must be monitored during the infusion and for at least one hour afterward for signs of infusion reactions, which can include symptoms like itching, rash, difficulty breathing, and fever. Infusion reactions can occur up to 24 hours post-infusion.
- Management of Reactions: If infusion reactions occur, the infusion rate may need to be slowed, or the infusion may be temporarily or permanently stopped depending on severity.
Infection Risk
- Increased Susceptibility: Ocrevus can increase the risk of serious infections, including upper and lower respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and reactivation of viral infections. Patients should be evaluated for any infections prior to treatment.
- Vaccination Precautions: Live vaccines should be avoided during treatment and until B-cell recovery occurs. Non-live vaccines should be administered at least two weeks prior to starting Ocrevus.
Contraindications
- Active Hepatitis B: Ocrevus is contraindicated in patients with active hepatitis B virus infection or a history of life-threatening infusion reactions to Ocrevus.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should discuss the risks and benefits of Ocrevus with their healthcare provider, as it may cross the placenta and affect the fetus. Effective contraception is recommended during treatment and for 12 months after the last infusion.
- Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding is not recommended while on Ocrevus, as the drug may be excreted in breast milk, and the effects on the nursing infant are unknown.
Other Medications
- Immunosuppressants: Caution is advised when using Ocrevus with other immunosuppressive therapies, as this can enhance the risk of infections and other side effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking.
Driving and Operating Machinery
- Uncertain Effects: It is not known whether Ocrevus affects the ability to drive or operate machinery. Patients should consult their healthcare provider regarding their specific situation.
General Considerations
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important, especially during and after infusions, to help manage potential side effects such as infusion reactions.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet can support overall health and immune function. Patients are encouraged to consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Alcohol Consumption: While not explicitly restricted, moderation in alcohol consumption is advisable, as excessive alcohol can affect immune function and overall health.
- Avoiding Live Vaccines: Patients should avoid live or live-attenuated vaccines during treatment and until B-cell recovery occurs, which is crucial for preventing infections.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Patients should discuss any dietary concerns or specific food interactions with their healthcare provider, especially if they have underlying health conditions or are on other medications that may have dietary implications.
Foods and Substances to Consider
Alcohol
- Moderation Recommended: While not explicitly prohibited, it is advisable to consume alcohol in moderation. Excessive alcohol can impair immune function and overall health.
Live Vaccines
- Avoidance Required: Patients should not receive live or live-attenuated vaccines during treatment and for at least 4 weeks before starting Ocrevus. This is crucial as the drug can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infections.
Supplements and Herbal Products
- Consultation Recommended: Some supplements and herbal products may interact with Ocrevus. Patients should discuss any vitamins, herbs, or supplements they are taking with their healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions.
General Healthy Eating
- Balanced Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and immune function during treatment.
Consultation with Healthcare Provider
- Individualized Advice: It is essential for patients to consult their healthcare provider for personalized dietary advice based on their health status and any other medications they may be taking.
Potential Effects on Nutrient Absorption
- Immunosuppression: Ocrevus works by depleting CD20-positive B cells, leading to immunosuppression. This can increase the risk of infections, including gastrointestinal infections, which may indirectly affect nutrient absorption if the digestive system is compromised.
- Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Some patients may experience gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, which can affect nutrient absorption. Diarrhea can lead to malabsorption of nutrients and dehydration, impacting overall nutritional status.
- Decreased Immunoglobulin Levels: Ocrevus may cause a decrease in certain immunoglobulins, which could potentially affect the body’s ability to respond to infections, including those that could impact the gut and nutrient absorption.
- Dietary Considerations: While no specific foods are restricted, maintaining a balanced diet is essential for supporting overall health and immune function during treatment. A healthy diet can help mitigate some of the risks associated with immunosuppression.
Use During Pregnancy
- Avoidance Recommended: Ocrevus should be avoided during pregnancy unless the potential benefits to the mother outweigh the risks to the fetus. There is limited data on the safety of Ocrevus in pregnant women, and no adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted.
- Reported Pregnancies: As of July 2023, 3,244 pregnancies have been reported in women treated with Ocrevus, with no evidence suggesting an increased risk of adverse pregnancy or infant outcomes. However, there are concerns about transient B-cell depletion in infants born to mothers exposed to anti-CD20 therapies.
- Ongoing Studies: The SOPRANINO and MINORE studies are currently evaluating the placental transfer of Ocrevus and its effects on infants.
Use During Breastfeeding
- Limited Data: There is limited information on the excretion of Ocrevus in breast milk. The SOPRANINO study is assessing the transfer of Ocrevus into breast milk and its effects on breastfeeding infants.
- Consideration of Benefits: The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be weighed against the mother’s clinical need for Ocrevus and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant.
- Infant Monitoring: Infants exposed to Ocrevus through breastfeeding should be monitored for normal B-cell levels and any adverse events, primarily infections.
Dosage
Ocrevus is administered as an intravenous (IV) infusion and is typically prescribed as follows:
- Initial Dosing: The first infusion consists of 600 mg, given as two separate infusions of 300 mg each, spaced two weeks apart. Each infusion lasts approximately 2.5 hours.
- Maintenance Dosing: After the initial doses, patients receive a single 600 mg infusion every six months. This infusion may take about 3.5 hours or longer, depending on the patient’s response and infusion rate.
- Missed Doses: If a patient misses an infusion appointment, they should contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible to reschedule and adjust the dosing schedule accordingly.
Storage
Ocrevus should be stored under the following conditions:
- Temperature: It must be kept in a refrigerator at a temperature between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- Protection from Light: The vial should be protected from light and should not be frozen.
- Expiration: Patients should check the expiration date on the vial before use and discard any unused portions as per local regulations.
Reviews
Ocrevus has received mixed reviews from patients, with an average rating of 5.0 out of 10 based on user experiences:
- Positive Experiences: About 39% of reviewers reported positive outcomes, noting significant improvements in symptoms and quality of life. Some patients experienced reduced fatigue and fewer relapses after starting treatment.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.