Sandostatin LAR octreotide 20mg Injection Imported in pakistan
Sandostatin LAR 20mg Injection Overview
Brand: Sandostatin
Active Ingredient: Octreotide Acetate
Manufacturer: Novartis
Price Range in Pakistan: Rs 33,000 to Rs 38,000
Indications
Acromegaly
Sandostatin LAR is primarily used to treat acromegaly, a disorder characterized by excessive growth hormone production. Symptoms include enlarged hands and feet, coarsening of facial features, and fatigue.
Gastrointestinal Tumors
It is also indicated for managing symptoms associated with certain gastrointestinal tumors, such as carcinoid tumors and VIPoma, which can cause severe diarrhea and flushing.
Mechanism of Action
Sandostatin LAR mimics somatostatin, a natural hormone that regulates hormone release in the body. By inhibiting excess growth hormone and hormone production from tumors, it helps alleviate symptoms and control tumor growth.
Dosage and Administration
- Starting Dose: 20mg administered intramuscularly every 4 weeks.
- Dosage Adjustments: After 2 months, the dose may be adjusted based on symptom control, with options to reduce to 10mg or increase to 30mg if necessary.
-
Original price was: ₨80,000.00.₨72,000.00Current price is: ₨72,000.00.
Description
Sandostatin LAR 20mg Injection Overview
Brand: Sandostatin
Active Ingredient: Octreotide Acetate
Manufacturer: Novartis
Price Range in Pakistan: Rs 33,000 to Rs 38,000
Indications
Acromegaly
Sandostatin LAR is primarily used to treat acromegaly, a disorder characterized by excessive growth hormone production. Symptoms include enlarged hands and feet, coarsening of facial features, and fatigue.
Gastrointestinal Tumors
It is also indicated for managing symptoms associated with certain gastrointestinal tumors, such as carcinoid tumors and VIPoma, which can cause severe diarrhea and flushing.
Mechanism of Action
Sandostatin LAR mimics somatostatin, a natural hormone that regulates hormone release in the body. By inhibiting excess growth hormone and hormone production from tumors, it helps alleviate symptoms and control tumor growth.
Dosage and Administration
- Starting Dose: 20mg administered intramuscularly every 4 weeks.
- Dosage Adjustments: After 2 months, the dose may be adjusted based on symptom control, with options to reduce to 10mg or increase to 30mg if necessary.
-
Key Benefits of Sandostatin LAR 20mg Injection
- Regulation of Growth Hormone: Sandostatin LAR effectively regulates excessive growth hormone production in patients with acromegaly, alleviating symptoms such as enlarged hands and feet, headaches, and fatigue.
- Management of Tumor Symptoms: It helps control symptoms associated with gastrointestinal tumors, such as carcinoid tumors and VIPoma, which can cause severe diarrhea and flushing.
- Long-Lasting Effects: The formulation allows for sustained release of the active ingredient, providing therapeutic effects that last for up to four weeks after a single injection.
- Improvement in Quality of Life: By managing hormone levels and reducing symptoms, Sandostatin LAR can significantly enhance the overall well-being and quality of life for patients.
- Potential Tumor Growth Control: It may slow down tumor growth in patients with neuroendocrine tumors, leading to better disease management.
Key Ingredients
- Active Ingredient: Octreotide Acetate
- A synthetic analog of somatostatin, which mimics the action of the natural hormone that regulates hormone secretion in the body.
- Excipients: The injection may contain other inactive ingredients that aid in the formulation and stability of the drug, although specific excipients are not detailed in the provided sources.
-
Mechanism of Action
Sandostatin LAR (octreotide acetate) exerts its effects by mimicking the action of the natural hormone somatostatin. Here’s how it works:
- Octreotide is a synthetic compound similar to somatostatin, a hormone naturally produced in the body that regulates the release of other hormones like growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin.
- In acromegaly, the pituitary gland produces excessive growth hormone. Sandostatin LAR acts like somatostatin, helping to regulate growth hormone release and bringing levels closer to normal.
- In certain tumors like carcinoid tumors and VIPoma, the tumors themselves produce excess hormones that cause symptoms. By mimicking somatostatin, Sandostatin LAR helps control the release of these hormones from the tumors.
- Sandostatin LAR is an even more potent inhibitor of growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin compared to natural somatostatin. It also suppresses the luteinizing hormone (LH) response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), decreases splanchnic blood flow, and inhibits the release of serotonin, gastrin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), secretin, motilin, and pancreatic polypeptide.
- The long-acting formulation of Sandostatin LAR allows for slow release of octreotide acetate from the injection site, reducing the need for frequent administration. This slow release occurs as the polymer biodegrades, primarily through hydrolysis.
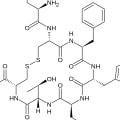
Chemical Structure of Octreotide (Sandostatin LAR)
Octreotide, the active ingredient in Sandostatin LAR, is a cyclic octapeptide. Its chemical structure can be described as follows:
- Chemical Name: L-Cysteinamide, D-phenylalanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-phenylalanyl-D-tryptophyl-L-lysyl-L-threonyl-N-[2-hydroxy-1(hydroxy-methyl)propyl]-, cyclic (2→7)-disulfide; [R-(R*,R*)].
- Molecular Formula: C₄₉H₆₆N₁₀O₁₀S₂
- Molecular Weight: 1019.3 g/mol
Amino Acid Sequence
The amino acid sequence of octreotide is crucial for its biological activity and is structured as follows:
- Sequence: Cys-D-Phe-Cys-Phe-Trp-Lys-Thr
Structural Features
- Cyclic Structure: The cyclic nature of octreotide is formed by a disulfide bond between two cysteine residues, which stabilizes the peptide and enhances its resistance to enzymatic degradation compared to natural somatostatin.
- Functional Groups: The presence of various functional groups, including hydroxyl and amine groups, contributes to its pharmacological properties.
 Octa-peptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologicallyMoreTrade namesSandostatin, Bynfezia Pen, Mycapssa, othersApproved UsageTreatment of growth hormone producing tumors, pituitary tumors, diarrhea, flushing, and glucagonomaAdministrationSubcutaneous injection, intramuscular injection, intravenous therapy, oral administration
Octa-peptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologicallyMoreTrade namesSandostatin, Bynfezia Pen, Mycapssa, othersApproved UsageTreatment of growth hormone producing tumors, pituitary tumors, diarrhea, flushing, and glucagonomaAdministrationSubcutaneous injection, intramuscular injection, intravenous therapy, oral administrationPharmacological Actions of Octreotide
Octreotide, a synthetic analog of somatostatin, exhibits several pharmacological actions that are beneficial in managing various medical conditions, particularly those related to hormone secretion. Here are the key pharmacological actions of octreotide:
- Inhibition of Hormone Secretion:
- Octreotide effectively inhibits the secretion of several hormones, including:
- Growth Hormone (GH): Reduces levels in patients with acromegaly.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Suppresses release from the anterior pituitary.
- Insulin and Glucagon: Modulates blood glucose levels by inhibiting insulin and glucagon secretion.
- Gastrointestinal Hormones: Reduces levels of serotonin, gastrin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), secretin, motilin, and pancreatic polypeptide, which helps in managing symptoms associated with gastrointestinal tumors.
- Octreotide effectively inhibits the secretion of several hormones, including:
- Reduction of Gastrointestinal Motility:
- Octreotide decreases gastrointestinal motility, which can alleviate symptoms such as diarrhea, particularly in patients with metastatic carcinoid tumors and VIPomas.
- Vasoconstriction:
- It induces vasoconstriction in blood vessels, which can help reduce portal pressure in conditions like portal hypertension and bleeding varices.
- Decrease in Splanchnic Blood Flow:
- By reducing blood flow to the digestive organs, octreotide helps manage symptoms of flushing and diarrhea associated with certain tumors.
- Gallbladder Effects:
- Octreotide inhibits gallbladder contractility and bile secretion, which can lead to potential gallstone formation in some patients.
- Analgesic Properties:
- It has been suggested that octreotide may have analgesic effects, likely acting as a partial agonist at the mu-opioid receptor, providing pain relief in certain conditions.
- Calcium Regulation:
- Octreotide increases calcium entry into cells via L-type calcium channels, which contributes to its action on smooth muscle contraction and hormone regulation.
Octreotide, the active ingredient in Sandostatin LAR, can interact with various medications. Here are some key drug interactions to be aware of:
Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
- Octreotide inhibits the secretion of insulin and glucagon. Therefore, blood glucose levels should be monitored when starting or adjusting the dose of Sandostatin LAR, and anti-diabetic treatment should be adjusted accordingly.
Cyclosporine
- Concomitant administration of octreotide injection with cyclosporine may decrease blood levels of cyclosporine, potentially resulting in transplant rejection.
Bradycardia-Inducing Drugs
- Octreotide can cause bradycardia. Concomitant administration of bradycardia-inducing drugs, such as beta-blockers, may have an additive effect. Dose adjustments of concomitant medication may be necessary.
Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4
- Limited data suggests somatostatin analogs like octreotide may decrease the metabolic clearance of compounds known to be metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, possibly due to growth hormone suppression. Drugs mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 with a low therapeutic index (e.g., quinidine, terfenadine) should be used with caution.
Lutetium Lu 177 Dotatate Injection
- Octreotide competitively binds to somatostatin receptors and may interfere with the efficacy of lutetium Lu 177 dotatate. Sandostatin LAR should be discontinued at least 4 weeks prior to each lutetium Lu 177 dotatate dose.
Additionally, octreotide has been associated with alterations in nutrient absorption, so it may affect the absorption of orally administered drugs.
Medications to Avoid with Octreotide
- Cimetidine: May alter the metabolism of octreotide, potentially affecting its efficacy.
- Ciclosporin: Co-administration can decrease blood levels of ciclosporin, increasing the risk of transplant rejection.
- Bromocriptine: Octreotide can increase the bioavailability of bromocriptine, which may lead to enhanced effects or side effects since both are used to treat acromegaly.
- Quinidine: This antiarrhythmic drug may have its effects altered by octreotide, increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
- Terfenadine: Co-administration may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias due to QT interval prolongation.
- Astemizole: Similar to terfenadine, it may lead to serious heart rhythm problems when used with octreotide.
- Cisapride: This gastrointestinal motility agent may have increased risk of cardiac side effects when taken with octreotide.
- Pimozide: This antipsychotic may have its effects enhanced, leading to increased risk of side effects.
- Sotalol: Another drug that can prolong the QT interval; caution is advised when used with octreotide.
- Disopyramide: This antiarrhythmic medication may interact with octreotide, increasing the risk of adverse cardiovascular effects.
- Ibutilide: Similar to other QT-prolonging agents, caution is warranted.
- Pentamidine: Potential for increased toxicity when used with octreotide.
Key Precautions with Octreotide (Sandostatin LAR)
- Gallbladder function: Treatment with octreotide may affect gallbladder function, leading to cholelithiasis (gallstones) in some patients. Periodic monitoring of the gallbladder is recommended.
- Glucose metabolism: Octreotide can affect blood glucose levels. Patients with diabetes should have their blood sugar levels monitored regularly, and adjustments to anti-diabetic medications may be necessary.
- Thyroid function: Long-term treatment with octreotide may affect thyroid function. Periodic monitoring of thyroid function is recommended.
- Cardiac function: Octreotide should be used with caution in patients at risk of cardiac disorders.
- Nutritional absorption: Octreotide may affect the absorption of some nutrients. Periodic monitoring is recommended.
- Allergic reactions: Patients should inform their healthcare providers if they have any allergies, as octreotide may contain ingredients that could cause allergic reactions.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The safety of octreotide during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established. Patients should consult with their doctor before using octreotide if they are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding.
Dietary Restrictions
There are no specific dietary restrictions associated with the use of octreotide. However, patients should maintain a balanced and nutritious diet to support overall health and minimize potential side effects.
Effects on Blood Sugar Levels
- Hypoglycemia:
- Clinical studies have shown that approximately 3% of patients may experience hypoglycemia while using Sandostatin. Symptoms can include confusion, dizziness, sweating, and weakness. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop below 70 mg/dL.
- Hyperglycemia:
- About 16% of patients may develop hyperglycemia. Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Hyperglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels rise above 140 mg/dL.
Monitoring and Management
- Regular Monitoring: Patients using Sandostatin, especially those with diabetes or at risk of blood sugar fluctuations, should have their blood glucose levels monitored regularly. Adjustments to diabetes medications may be necessary based on these readings.
- Consulting Healthcare Providers: If patients experience symptoms of either hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, they should consult their doctor for potential adjustments in their treatment plan.
Pregnancy
- Risk Summary: Limited data on the use of octreotide during pregnancy are insufficient to determine a definitive risk for major birth defects or miscarriage. Animal studies have shown no adverse developmental effects when octreotide was administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses significantly higher than the maximum recommended human dose. However, a slight reduction in body weight gain was observed in pregnant rats, and transient growth retardation was noted in offspring, which may be linked to growth hormone inhibition.
- Human Data: In postmarketing reports, some women have been exposed to octreotide during the first trimester, with no congenital malformations reported in cases with known outcomes. Nevertheless, due to the limited number of cases, the risk cannot be fully assessed.
- FDA Classification: Octreotide is classified as FDA pregnancy risk category B, indicating that animal reproduction studies have not demonstrated a risk to the fetus, but adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women are lacking.
Breastfeeding
- Lactation Risk: There is currently no information available on the presence of octreotide in human milk, nor its effects on a breastfed infant or on milk production. Studies in lactating rats have shown that octreotide can transfer into milk, but the concentrations were low compared to plasma.
- Caution Advised: Due to the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, octreotide should be used cautiously during breastfeeding. The benefits of breastfeeding should be weighed against the clinical need for octreotide in the mother.
Dosage of Sandostatin LAR
Recommended Dosage
- Initial Dose: For patients not currently receiving octreotide, the recommended starting dose is 20 mg administered intramuscularly every 4 weeks.
- Adjustment:
- If symptoms are adequately controlled, consider reducing the dose to 10 mg every 4 weeks.
- If symptoms are not adequately controlled, the dose may be increased to 30 mg every 4 weeks.
- Dosages higher than 30 mg are not recommended.
Special Populations
- Renal Impairment: In patients requiring dialysis, the starting dose should be 10 mg every 4 weeks. For other patients with renal impairment, the starting dose is typically 20 mg every 4 weeks.
Administration
- Sandostatin LAR should be administered by a trained healthcare provider. It is available in single-dose kits containing a vial of the drug and a prefilled syringe for diluent.
Storage of Sandostatin LAR
- Storage Conditions: Sandostatin LAR should be stored in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). It should not be frozen.
- Preparation: The product should be prepared immediately before use. If the prepared suspension is not used right away, it should be stored at room temperature (not exceeding 25°C or 77°F) and used within 24 hours.
Reviews of Sandostatin LAR
Patient Feedback
- Many patients report significant improvement in symptoms related to acromegaly and neuroendocrine tumors, such as reduced flushing and diarrhea.
Dosage Guidelines
- For Patients Not Currently Receiving Sandostatin:
- Acromegaly: Start with Sandostatin Injection (50 mcg three times daily) for 2 weeks, then switch to Sandostatin LAR Depot (20 mg) intramuscularly every 4 weeks for 3 months.
- Carcinoid Tumors and VIPomas: Begin with Sandostatin Injection (100 to 600 mcg/day) for 2 weeks, then switch to Sandostatin LAR Depot (20 mg) every 4 weeks for 2 months.
- For Patients Currently Receiving Sandostatin Injection:
- Acromegaly: Administer 20 mg every 4 weeks for 3 months.
- Carcinoid Tumors and VIPomas: Administer 20 mg every 4 weeks for 2 months.
Adjustments
After the initial treatment period, the dosage may be adjusted based on clinical response, with potential increases to 30 mg or decreases to 10 mg, but administration should not exceed every 4 weeks.
Administration Method
Sandostatin LAR must be administered intramuscularly by a trained healthcare provider, specifically in the gluteal region, and injection sites should be rotated to avoid irritation.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.