Seroquel 100mg 30’ct (quetipapine) In Pakistan
Seroquel (Quetiapine) Overview
Seroquel, generically known as quetiapine, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used primarily to treat mental health disorders.
Indications
Seroquel is commonly prescribed for:
- Schizophrenia: Helps manage symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
- Bipolar Disorder: Effective in treating both manic and depressive episodes.
Availability in Pakistan
Dosage Forms
- Seroquel 100 mg: Available in packs of 30 tablets.
- Other Dosages: Seroquel is also available in lower dosages, such as 25 mg.
Pricing
- Seroquel 100 mg (30 tablets): Approximately Rs. 1713.22.
- Seroquel 25 mg (30 tablets): Approximately Rs. 485.84.
Common Side Effects
Patients may experience side effects, which can include:
- Somnolence: Increased drowsiness or sleepiness.
- Dry Mouth: A common side effect that may require management.
- Fatigue: General tiredness or lack of energy.
- Constipation: Digestive issues may arise.
- Weight Gain: Long-term use can lead to changes in weight.
Important Considerations
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting medication.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor effectiveness and side effects.
-
Original price was: ₨5,000.00.₨4,000.00Current price is: ₨4,000.00.
Description
Seroquel (Quetiapine) Overview
Seroquel, generically known as quetiapine, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used primarily to treat mental health disorders.
Indications
Seroquel is commonly prescribed for:
- Schizophrenia: Helps manage symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
- Bipolar Disorder: Effective in treating both manic and depressive episodes.
Availability in Pakistan
Dosage Forms
- Seroquel 100 mg: Available in packs of 30 tablets.
- Other Dosages: Seroquel is also available in lower dosages, such as 25 mg.
Pricing
- Seroquel 100 mg (30 tablets): Approximately Rs. 1713.22.
- Seroquel 25 mg (30 tablets): Approximately Rs. 485.84.
Common Side Effects
Patients may experience side effects, which can include:
- Somnolence: Increased drowsiness or sleepiness.
- Dry Mouth: A common side effect that may require management.
- Fatigue: General tiredness or lack of energy.
- Constipation: Digestive issues may arise.
- Weight Gain: Long-term use can lead to changes in weight.
Important Considerations
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting medication.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor effectiveness and side effects.
Key Benefits
- Effective treatment for manic and depressive episodes in bipolar disorder
- Helps manage symptoms of schizophrenia like hallucinations and delusions
- Can be used short-term or long-term depending on the condition being treated
Key Ingredients
The active ingredient in Seroquel is quetiapine fumarate. The inactive ingredients for Seroquel XR (extended-release) include lactose monohydrate.Seroquel is available in Pakistan in various dosages, including 25 mg and 100 mg tablets. The price for a pack of 30 Seroquel 100 mg tablets is approximately Rs. 1713.22. Seroquel (quetiapine) has several known interactions with other medications, which can affect its efficacy and safety. Here are the key points regarding these interactions:
Known Drug Interactions
- Total Interactions: Seroquel is known to interact with 710 medications, categorized as follows:
- Major Interactions: 146
- Moderate Interactions: 560
- Minor Interactions: 4.
Commonly Checked Interactions
Some frequently checked medications that may interact with Seroquel include:
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., alprazolam, lorazepam): Increased sedation risk.
- Antidepressants (e.g., fluoxetine, duloxetine): Potential for increased side effects.
- Antihypertensives (e.g., lisinopril): May enhance hypotensive effects.
- Anticonvulsants (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine): Can decrease Seroquel’s effectiveness.
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole): Increase Seroquel levels, requiring dose adjustments.
- CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., St. John’s Wort, rifampin): Decrease Seroquel levels, potentially necessitating higher doses.
Alcohol and Food Interactions
- Alcohol: Can enhance the sedative effects of Seroquel, increasing the risk of drowsiness and cognitive impairment.
- Grapefruit: Should be avoided as it can increase Seroquel levels in the body, raising the risk of side effects.
Disease Interactions
Seroquel also has interactions with certain health conditions, including:
- QT Prolongation: Risk of heart rhythm issues.
- CNS Depression: Increased risk when combined with other CNS depressants.
- Diabetes and Hyperglycemia: Can exacerbate these conditions.
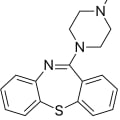
 QuetiapineAtypical antipsychotic medicationMorePrimary usesTreatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorderCommon side effectsSleepiness, constipation, weight gain, and dry mouthBrand nameSeroquel among othersSeroquel (quetiapine) operates through a complex mechanism of action that primarily involves its interactions with various neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. Here are the key aspects of its mechanism:
QuetiapineAtypical antipsychotic medicationMorePrimary usesTreatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorderCommon side effectsSleepiness, constipation, weight gain, and dry mouthBrand nameSeroquel among othersSeroquel (quetiapine) operates through a complex mechanism of action that primarily involves its interactions with various neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. Here are the key aspects of its mechanism:Mechanism of Action
Receptor Interactions
- Dopamine Receptors:
- Dopamine D2 Antagonism: Seroquel acts as an antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors, which helps alleviate symptoms of psychosis and mood disorders. It has a low affinity for these receptors, allowing for rapid dissociation, which is associated with a lower incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) compared to other antipsychotics.
- Serotonin Receptors:
- Serotonin 5-HT1A Partial Agonist: This action may contribute to its antidepressant effects and anxiolytic properties.
- Serotonin 5-HT2A Antagonism: This antagonistic effect is a common feature of atypical antipsychotics, helping to balance serotonin levels and reduce psychotic symptoms.
- Histamine Receptors:
- Histamine H1 Antagonism: This interaction can lead to sedative effects, which is beneficial for patients experiencing insomnia or agitation.
- Adrenergic Receptors:
- Alpha-1 and Alpha-2 Antagonism: This can result in hypotensive effects, which may be a consideration in patients with low blood pressure.
Pharmacodynamics
The unique combination of these receptor interactions allows Seroquel to effectively manage symptoms of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder while minimizing the risk of certain side effects typically associated with other antipsychotics.

Key Precautions
- Medical History: Inform your healthcare provider about your complete medical history, especially if you have:
- Heart problems (e.g., heart disease, irregular heart rhythms)
- High or low blood pressure
- Diabetes or high cholesterol
- Seizure disorders
- Thyroid issues (e.g., underactive thyroid)
- Eye problems (e.g., glaucoma or cataracts)
- Liver conditions (e.g., hepatitis or fatty liver disease)
- History of low white blood cell counts
- Elderly Patients: Increased mortality has been noted in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis who are treated with antipsychotic medications, including Seroquel.
- Suicidal Thoughts: Monitor for any changes in mood or behavior, especially in young adults and adolescents, as they may experience increased suicidal thoughts when starting treatment.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Seroquel can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing. Caution is advised when moving from sitting to standing.
- Seizures: Use with caution if you have a history of seizures, as Seroquel may lower the seizure threshold.
- Dehydration and Temperature Regulation: Antipsychotic medications can affect how your body regulates temperature, increasing the risk of dehydration, especially in hot weather or during exercise.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, as Seroquel may not be safe during these times.
Dietary Restrictions
- Alcohol: Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Seroquel, as it can enhance the sedative effects and increase the risk of serious side effects.
- Grapefruit: It is advisable to avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice, as they can increase blood levels of Seroquel, potentially leading to increased side effects.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: If you have diabetes, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential, as Seroquel may cause high blood sugar.
- Hydration: Maintain adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.
- Dietary Fat: Be mindful of dietary fat intake, as Seroquel may cause weight gain and changes in cholesterol levels.
Overview of Interactions
- Total Interactions: Seroquel is known to interact with 710 medications, categorized into:
- Major Interactions: 146
- Moderate Interactions: 560
- Minor Interactions: 4
Commonly Checked Interactions
Some frequently checked medications that may interact with Seroquel include:
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., alprazolam, lorazepam): Increased sedation risk when combined.
- Antidepressants (e.g., fluoxetine, duloxetine): Potential for enhanced side effects.
- Anticonvulsants (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine): Can decrease the effectiveness of Seroquel.
- Antihypertensives (e.g., lisinopril): May enhance hypotensive effects.
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole): Can significantly increase Seroquel levels, requiring dose adjustments.
- CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John’s Wort): Can decrease Seroquel levels, potentially necessitating higher doses.
Specific Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
- Examples: Ketoconazole, itraconazole.
- Effect: Increase Seroquel levels; may require dose reduction.
- CYP3A4 Inducers:
- Examples: Phenytoin, carbamazepine, St. John’s Wort.
- Effect: Decrease Seroquel levels; may require dose increase.
- Anticholinergic Drugs:
- Effect: Increased risk of gastrointestinal issues; caution is advised.
- Anti-arrhythmic Drugs:
- Examples: Quinidine, procainamide, sotalol.
- Effect: Risk of QT prolongation and serious heart rhythm problems.
- Parkinson’s Medications:
- Examples: Levodopa, pramipexole.
- Effect: Quetiapine may block the effects of these medications.
Alcohol and Food Interactions
- Alcohol: Can enhance the sedative effects of Seroquel, increasing the risk of drowsiness and cognitive impairment.
- Grapefruit: Should be avoided, as it can increase Seroquel levels, raising the risk of side effects.
Dosage
Schizophrenia
- Starting Dose:
- Day 1: 25 mg twice per day
- Day 2: 50 mg twice per day
- Day 3: 100 mg twice per day
- Day 4: 100 mg three times per day
- Maintenance Dose: Typically 400 mg to 800 mg per day, divided into two or three doses. Maximum dose is 800 mg per day.
Bipolar Disorder
- Manic Episodes:
- Day 1: 50 mg twice per day
- Day 2: 100 mg twice per day
- Day 3: 150 mg twice per day
- Day 4: 200 mg twice per day
- Maintenance Dose: Usually 400 mg to 800 mg per day.
Depressive Episodes
- Starting Dose:
- Day 1: 50 mg once per day
- Day 2: 100 mg once per day
- Day 3: 200 mg once per day
- Day 4: 300 mg once per day
Storage
- Seroquel should be stored at room temperature, away from excess moisture and heat. Always check the expiration date provided by the pharmacist on the medication label and dispose of any expired medications properly.
Reviews
General Sentiment
- Effectiveness: User ratings vary widely, with some finding significant relief from symptoms and others reporting severe side effects.
- Average Ratings:
- Schizophrenia: 6.4/10 based on 46 reviews.
- General user ratings on WebMD average around 2.3 to 3.3/10, indicating mixed experiences.
Positive Experiences
- Many users report improvements in anxiety, sleep quality, and overall mood stabilization after starting Seroquel, especially at lower doses.
- Starting Dose:







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.