Xanax Alprazolaam 1mg 30’ct tablets in Pakistan
Xanax (Alprazolam) 1 mg Tablets in Pakistan
Overview
Xanax, with the active ingredient alprazolam, is a medication commonly prescribed for anxiety and panic disorders. It is a part of the benzodiazepine class of drugs, which work by calming the brain and nerves.
Availability
- Formulation: 1 mg tablets
- Pack Size: Available in packs of 30 tablets
Pricing
- Approximate Cost: Rs. 167 for a pack of 30 tablets
Uses
- Primary Indications:
- Anxiety disorders
- Panic disorders
Important Considerations
- Controlled Substance: Xanax is classified as a controlled substance in Pakistan due to its potential for abuse and dependence.
- Prescription Requirement: It is essential to use Xanax under the supervision of a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Conclusion
Xanax can be an effective treatment for anxiety and panic disorders when used responsibly. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting any medication.
Original price was: ₨6,500.00.₨5,999.00Current price is: ₨5,999.00.
Description
Xanax (Alprazolam) 1 mg Tablets in Pakistan
Overview
Xanax, with the active ingredient alprazolam, is a medication commonly prescribed for anxiety and panic disorders. It is a part of the benzodiazepine class of drugs, which work by calming the brain and nerves.
Availability
- Formulation: 1 mg tablets
- Pack Size: Available in packs of 30 tablets
Pricing
- Approximate Cost: Rs. 167 for a pack of 30 tablets
Uses
- Primary Indications:
- Anxiety disorders
- Panic disorders
Important Considerations
- Controlled Substance: Xanax is classified as a controlled substance in Pakistan due to its potential for abuse and dependence.
- Prescription Requirement: It is essential to use Xanax under the supervision of a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Conclusion
Xanax can be an effective treatment for anxiety and panic disorders when used responsibly. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting any medication.
Key Benefits of Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Effective Anxiety Relief: Xanax is primarily prescribed for managing generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder, providing quick relief from acute anxiety symptoms and panic attacks.
- Fast-Acting: The medication acts rapidly, making it suitable for immediate relief in stressful situations, which is particularly beneficial for those experiencing severe anxiety or panic episodes.
- Muscle Relaxation: In addition to its primary uses, Xanax can also serve as a muscle relaxant, helping to alleviate tension in the body.
- CNS Depression: As a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, Xanax helps to slow down brain activity, promoting a sense of calm and relaxation.
- Off-Label Uses: While not officially approved for all of them, Xanax is sometimes used off-label for conditions such as insomnia and temporary anxiety related to various medical conditions.
Key Ingredients
- Active Ingredient:
- Alprazolam: This is the primary active ingredient in Xanax, belonging to the benzodiazepine class of medications. It works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that promotes calmness in the brain.
- Inactive Ingredients: While specific inactive ingredients can vary by manufacturer, common components may include binders, fillers, and coloring agents used to formulate the tablet. These ingredients are generally not disclosed in detail in standard references but are essential for the tablet’s stability and effectiveness.

Mechanism of Action of Xanax (Alprazolam)
Xanax (alprazolam) is a benzodiazepine that exerts its effects primarily through its action on the central nervous system (CNS). Here’s a detailed explanation of its mechanism of action:
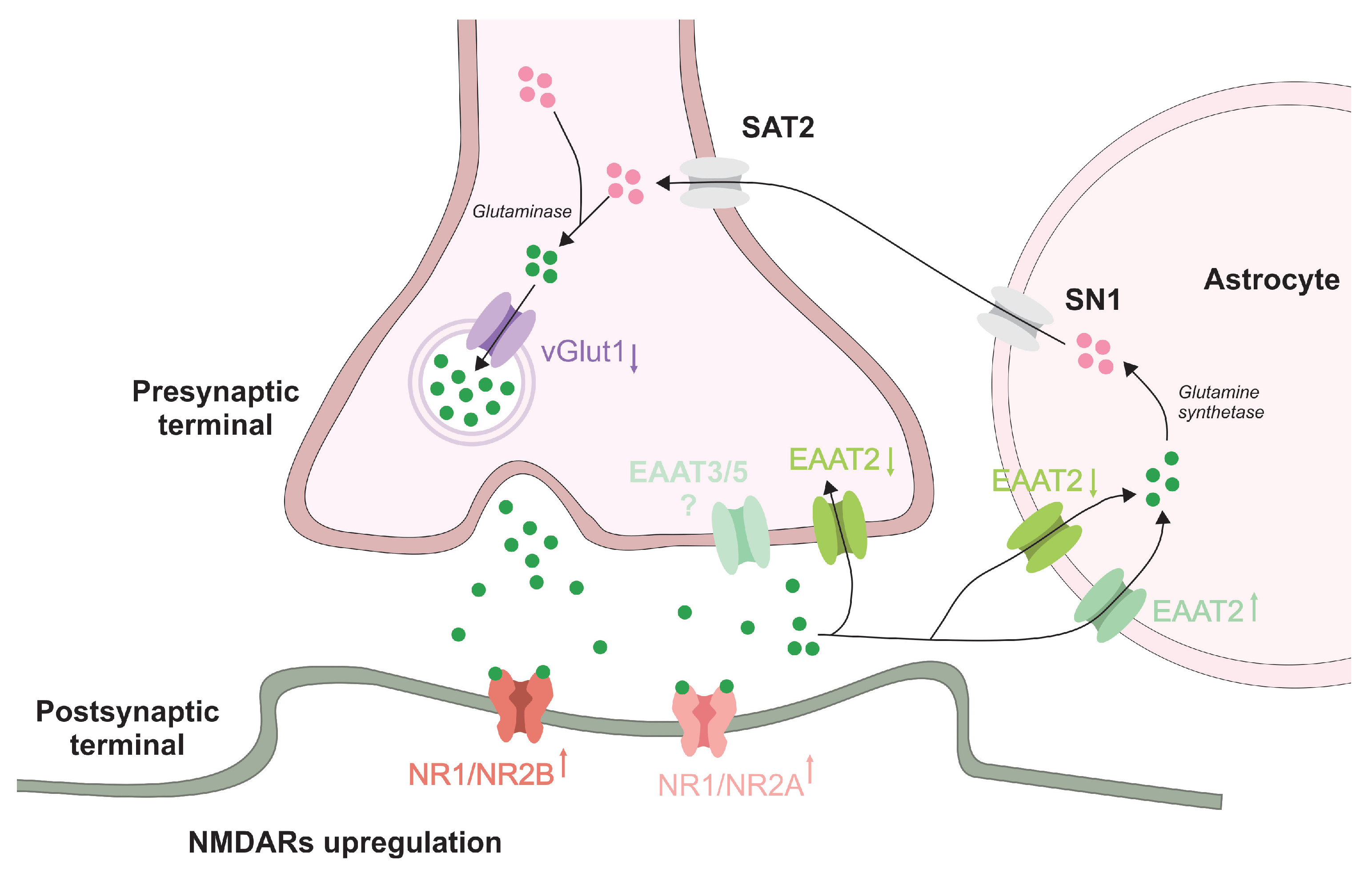
Interaction with GABA Receptors
- GABAergic Activity: Xanax enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It binds to specific sites on the GABA-A receptor, which is crucial for its anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) and sedative effects.
- Chloride Ion Influx: When GABA binds to its receptor, it opens a channel that allows chloride ions to enter the neuron. This influx of negatively charged chloride ions makes the neuron less excitable, leading to a calming effect on the nervous system. Xanax acts as a “booster” to GABA’s action, allowing more chloride ions to enter the neuron and further inhibiting neuronal excitability.
Central Nervous System Effects
- Sedation and Relaxation: By enhancing GABA activity, Xanax produces sedative and muscle relaxant effects, which help alleviate anxiety and panic symptoms.
- Dose-Dependent Effects: The effects of Xanax are dose-dependent, meaning that higher doses can lead to increased sedation and a greater reduction in anxiety symptoms. However, this also raises the risk of side effects and potential dependence.
Subtype Receptor Interactions
- Benzodiazepine Receptor Subtypes: Xanax interacts with different subtypes of benzodiazepine receptors, which are associated with various effects:
- Alpha-1 Subtype: Primarily linked to sedative effects.
- Alpha-2 Subtype: Associated with anxiolytic effects.
- Alpha-5 Subtype: Involved in cognitive functions and memory.
Key Precautions for Xanax (Alprazolam)
- Medical History: Inform your healthcare provider about your complete medical history, especially if you have conditions such as:
- Glaucoma
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Lung disease (e.g., COPD)
- History of substance use disorder
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Xanax can be harmful during pregnancy and is not recommended while breastfeeding. It may cause withdrawal symptoms in newborns if taken late in pregnancy. Consult your doctor if you become pregnant or are planning to breastfeed while on this medication.
- Age Considerations: Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of Xanax, increasing the risk of falls and coordination issues. A lower dose may be necessary.
- Driving and Operating Machinery: Xanax can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until you know how the medication affects you.
- Alcohol and Drug Interactions: Avoid alcohol and recreational drugs (including cannabis) while taking Xanax, as they can enhance sedative effects and increase the risk of severe side effects, including respiratory depression.
- Dosage and Withdrawal: Do not change your dosage or stop taking Xanax abruptly without consulting your doctor, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms. A gradual dose reduction may be necessary.
- Surgery: Inform your healthcare provider or dentist about your Xanax use before any surgical procedures, including dental surgery.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor for side effects and adjust the dosage as needed.
Dietary Restrictions
- Grapefruit Products: Avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking Xanax, as it can increase the risk of side effects by affecting drug metabolism.
- St. John’s Wort: This herbal supplement may lower the effectiveness of Xanax. Consult your doctor before taking any herbal supplements.
While taking Xanax (alprazolam), it’s important to avoid certain foods and beverages that can interact with the medication:
Grapefruit and Grapefruit Juice
- Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can interact with Xanax and lead to potentially dangerous side effects.
- Advise patients to avoid grapefruit juice and grapefruit during alprazolam treatment.
Alcohol
- Avoid alcoholic drinks while taking Xanax.
- Alcohol may increase dizziness and drowsiness.
Other Dietary Restrictions
- There are no other specific dietary restrictions mentioned for Xanax, but it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist about any potential interactions with the foods you consume.
Xanax and Ibuprofen
- Safety: It is generally considered safe to take ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) while using Xanax. There are no significant interactions reported between these two medications, meaning they can be used together without major concerns for most individuals.
- Precautions: While ibuprofen is safe, caution is advised if taking other medications that may interact with Xanax, particularly those that are CNS depressants, as they can enhance side effects like drowsiness and dizziness.
Xanax and Acetaminophen
- Safety: Similar to ibuprofen, acetaminophen (Tylenol) is typically safe to use alongside Xanax. There are no known significant interactions that would pose a risk when these medications are taken together.
- Considerations: As with ibuprofen, it’s important to avoid combining Xanax with other medications that could have sedative effects, especially opioids, which can lead to severe respiratory depression and other serious side effects.
General Recommendations
- Consult Healthcare Provider: Always discuss with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting any new medication, including over-the-counter drugs, while taking Xanax.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Be vigilant for any increased side effects such as excessive drowsiness or confusion when combining Xanax with other medications, even those considered safe.
- Avoid Opioids: Do not combine Xanax with opioid pain relievers unless specifically directed by a healthcare professional, due to the high risk of severe side effects and respiratory depression.
Use During Pregnancy
Risks Associated with Xanax
- Dependence and Withdrawal: Xanax can lead to physical dependence in pregnant women, which may result in withdrawal symptoms for the newborn, known as Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS). Symptoms can include irritability, difficulty feeding, and seizures.
- Congenital Disabilities: Research indicates that using Xanax during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, may be associated with an increased risk of congenital disabilities, such as cleft palate and microcephaly (abnormally small head circumference) .
- Fetal Harm: Xanax crosses the placenta, potentially affecting fetal development. It has been linked to risks such as neonatal depression, which can manifest as depressed breathing and other complications at birth.
- Pregnancy Category: Xanax is classified as a Category D medication by the FDA, indicating that there is evidence of risk to the fetus, but the benefits may outweigh the risks in certain situations.
Recommendations
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should discuss their medication regimen with their healthcare provider. The decision to continue or discontinue Xanax should be made based on a thorough evaluation of risks and benefits.
- Avoid Abrupt Discontinuation: If a woman is taking Xanax and becomes pregnant, she should not stop taking the medication abruptly due to the risk of withdrawal. Instead, a healthcare provider should guide a safe tapering plan if discontinuation is necessary.
Use During Breastfeeding
Risks Associated with Xanax
- Excretion in Breast Milk: Xanax is excreted in breast milk, and infants exposed to it may experience sedation, poor feeding, and weight gain issues.
- Potential Side Effects: Infants may show signs of sedation or withdrawal symptoms if the mother takes Xanax while breastfeeding. This can lead to complications in infant health and development.
Recommendations
- Avoid Breastfeeding: Due to the potential risks of sedation and withdrawal in infants, it is generally recommended that women do not breastfeed while taking Xanax. Consulting with a healthcare provider for alternative treatments is advisable.
Dosage of Xanax (Alprazolam)
Recommended Dosages
- For Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
- Starting Dose: 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg, administered three times daily.
- Maximum Dose: Up to 4 mg per day, divided into multiple doses. Adjustments can be made every 3 to 4 days based on response.
- For Panic Disorder:
- Starting Dose: 0.5 mg three times daily.
- Maximum Dose: Typically ranges from 1 mg to 10 mg daily, with an average of about 5 mg to 6 mg daily. Increments should not exceed 1 mg per day.
Administration
- Xanax is taken orally and can be absorbed quickly, with effects felt within 5 to 10 minutes for some individuals. The peak effects usually occur within 1 to 2 hours after ingestion.
Important Notes
- Always follow the prescribed dosage by a healthcare provider, and do not adjust the dosage without consultation.
- Gradual tapering is recommended when discontinuing Xanax to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Storage of Xanax
- Temperature: Store at controlled room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Protection: Keep in a tightly closed container, away from moisture and light.
- Disposal: Follow local regulations for medication disposal to ensure safety.
User Reviews and Experiences
General Feedback
- Effectiveness: Many users report significant relief from anxiety and panic symptoms, often rating their experience highly. For instance, one user mentioned that Xanax has been a “miracle drug” for managing panic attacks and anxiety over several years.
- Long-Term Use: Some individuals have taken Xanax for extended periods (e.g., over 20 years) without needing to increase their dosage, indicating its effectiveness in managing their conditions.
Concerns and Side Effects
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Users have expressed concerns about withdrawal symptoms when tapering off Xanax, including anxiety resurgence and physical symptoms like twitching and vomiting.
- Dependence: There are reports of individuals feeling dependent on Xanax for daily functioning, highlighting the importance of careful management and monitoring by healthcare providers.
- Medical History: Inform your healthcare provider about your complete medical history, especially if you have conditions such as:







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.